IBAN vs BIC: What They Mean and Why They Matter for International Payments
Learn what IBAN and BIC mean, how they differ, and why they are essential for fast and accurate international payments.
Introduction
If you’ve ever made or received an international payment, you’ve likely been asked for an IBAN and BIC.
For many businesses, these codes feel like administrative details — until a payment is delayed, rejected, or returned because one of them was missing or incorrect.
Understanding what IBAN and BIC actually mean, how they work together, and why banks rely on them is essential for anyone handling cross-border payments.
This guide explains both clearly, without jargon.
What Is an IBAN?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number.
It identifies a specific bank account in international transactions.
An IBAN is not random. It follows a strict structure that includes:
- A country code (e.g. GB, DE, FR)
- Check digits for validation
- A bank identifier
- The individual account number
In simple terms, the IBAN tells banks exactly which account should receive the money.
Why IBAN Is Important
- Ensures payments are routed to the correct account
- Reduces manual processing and errors
- Enables faster, automated handling of international payments
- Is mandatory for euro payments within SEPA
If an IBAN is incorrect, the payment may fail validation before it even leaves the sending bank.
What Is a BIC?
BIC stands for Bank Identifier Code (also known as a SWIFT code).
While the IBAN identifies the account, the BIC identifies the bank itself.
A BIC typically includes:
- Bank code
- Country code
- Location code
- Optional branch code
The BIC tells the payment network which financial institution should receive the payment instruction.
Why BIC Is Important
- Routes payments to the correct bank
- Is essential for global SWIFT payments
- Helps intermediary banks process payments correctly
- Reduces the risk of misrouting
Without a BIC, banks may not know where to send the payment instruction — especially outside Europe.
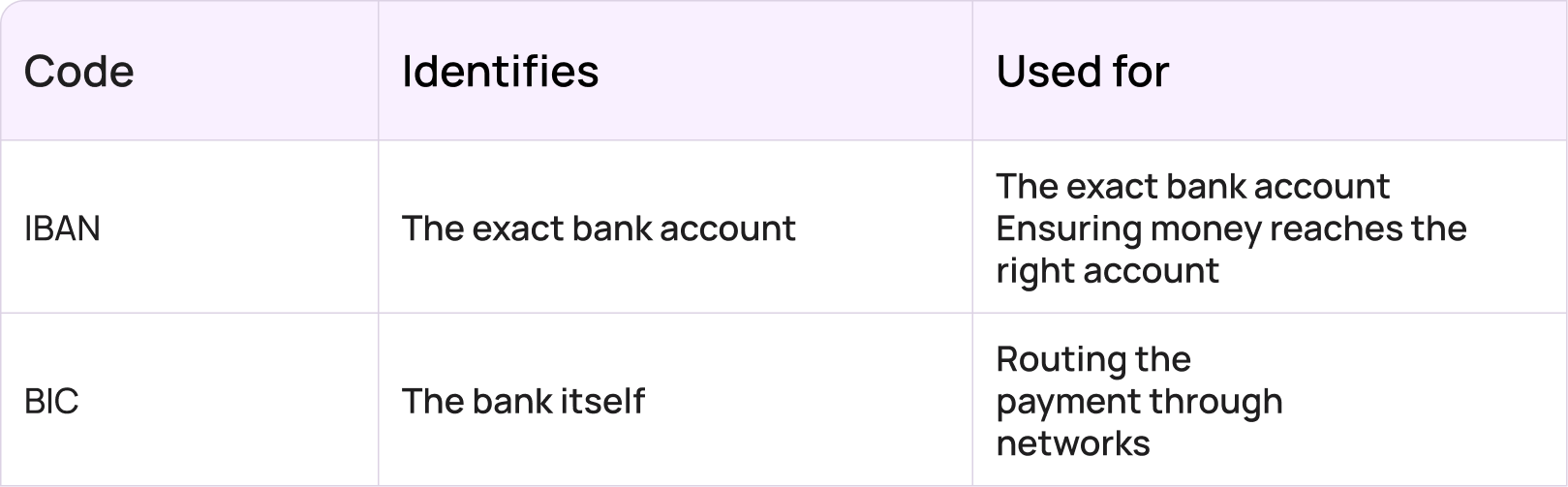
IBAN vs BIC: What’s the Difference?
The simplest way to understand IBAN vs BIC is this:
- IBAN = the account
- BIC = the bank
They serve different purposes but work together
For many European payments, the IBAN alone is sufficient. For global payments, IBAN and BIC together are often required.
When Do You Need IBAN and BIC?
You typically need IBAN and BIC when:
- Making international payments
- Sending or receiving EUR payments
- Using the SWIFT network
- Paying suppliers or employees abroad
- Receiving payments from overseas clients
In SEPA payments (EUR within Europe), banks often rely on the IBAN alone. Outside SEPA, the BIC is still critical for correct routing.
Why Incorrect IBAN or BIC Causes Delays
International payments move through multiple systems and sometimes multiple banks. If IBAN or BIC details are wrong:
- Payments may be rejected automatically
- Manual repair fees can be charged
- Funds may be returned days later
- Intermediary banks may deduct fees
- Settlement can be delayed significantly
Even a single incorrect character can cause problems.
This is why many modern payment platforms validate IBAN and BIC automatically before sending a payment.
How IBAN and BIC Improve Payment Security
Beyond routing, IBAN and BIC also support security:
- Built-in check digits reduce fraud and typos
- Structured formats enable automated verification
- Clear bank identification limits misdirection
- Reduced manual handling lowers operational risk
These standards are one of the reasons international payments are safer today than they were decades ago.
IBAN, BIC, and Modern Payment Platforms
Modern financial platforms still rely on IBAN and BIC, even when the user experience feels instant.
Behind the scenes, these identifiers:
- Connect platforms to traditional banking infrastructure
- Enable integration with SEPA, SWIFT, and domestic rails
- Allow faster compliance and reconciliation
- Support cross-border scalability
New technology improves speed and transparency — but IBAN and BIC remain foundational.
Common Questions About IBAN and BIC
Is IBAN the same as an account number?
No. An IBAN includes the account number, plus country and bank identifiers.
Can a payment be sent without a BIC?
Sometimes, within SEPA. For global payments, a BIC is usually required.
Are IBAN and BIC used worldwide?
IBAN is mainly used in Europe and a few other regions. BIC (SWIFT) is global.
Do IBAN and BIC expire?
No, but they can change if a bank restructures or merges.
Why Businesses Should Care
For businesses making international payments, understanding IBAN and BIC helps:
- Reduce failed payments
- Avoid unnecessary fees
- Speed up settlements
- Improve supplier relationships
- Minimise operational risk
They are not just technical codes — they are the language banks use to move money accurately.
Final Thoughts
IBAN and BIC may look like strings of letters and numbers, but they are essential building blocks of the global payments system.
Knowing how IBAN and BIC work — and using them correctly — is one of the simplest ways to make international payments faster, safer, and more predictable.
For any business operating across borders, that knowledge is a real advantage.

