Bank or Fintech: Key Differences from a User Perspective
Bank or fintech — which is best for international payments? One is a traditional choice, the other a modern alternative. This article explores how banks and fintechs differ for everyday users.
Bank or fintech — which is the right choice for making international payments? One is a traditional, familiar place you’ve been going to for years. The other is a new, trendy spot that everyone’s talking about. In this article, we will examine the key ways banks and fintech companies are different, focusing on what matters to you, the everyday user.
Account Opening Process
One of the biggest differences between banking institutions and fintech enterprises is how you open an account. By learning these distinctions, you can select the option that best aligns with your preferences, whether you value convenience, speed, or a more personal touch.
What distinguishes the process of opening an IBAN account with a traditional bank from a fintech company?
Banks: The old-school way
Opening a bank account traditionally requires visiting a physical office, where you’ll need to complete various steps, including:
- Visiting the branch during business hours;
- Bringing multiple forms of identification, such as your passport or driver’s license;
- Manually filling out paperwork;
- Waiting for approval, which could take several days.
The process is akin to the Sorting Hat ceremony at Hogwarts, where your identity and credentials must be validated before you are officially sorted into your new financial house.
+ This face-to-face process has been the standard way banks welcome new customers, reflecting a more conventional and secure identity verification procedure and setting up accounts.
– It can be time-consuming and inconvenient, especially if you have a busy schedule or live far from a bank office, requiring physical visits, which can delay the account activation process.
Fintech: The digital-first approach
Fintech companies have redefined the onboarding experience by offering seamless digital workflows. Users can complete the process from the comfort of their homes:
- Open an account from your smartphone or computer;
- Upload photos of your ID;
- Fill out forms digitally;
- Get approved in minutes or hours, not days.
Initiating an account with a fintech company is like entering the Matrix: a digital gateway where you can effortlessly plug in and get started, bypassing the cumbersome physical world of paperwork and waiting.
+ The process of setting up an account can be completed from any location, utilising advanced remote onboarding technologies and automated Know Your Customer (KYC) verification procedures.
– However, the reliance on biometric authentication and electronic identity verification might raise concerns about data security and the thoroughness of authentication.
The key feature of Transferra’s approach to account opening is our user-centric registration process that allows for rapid setup of both individual and business profiles through a simple, digital interface.
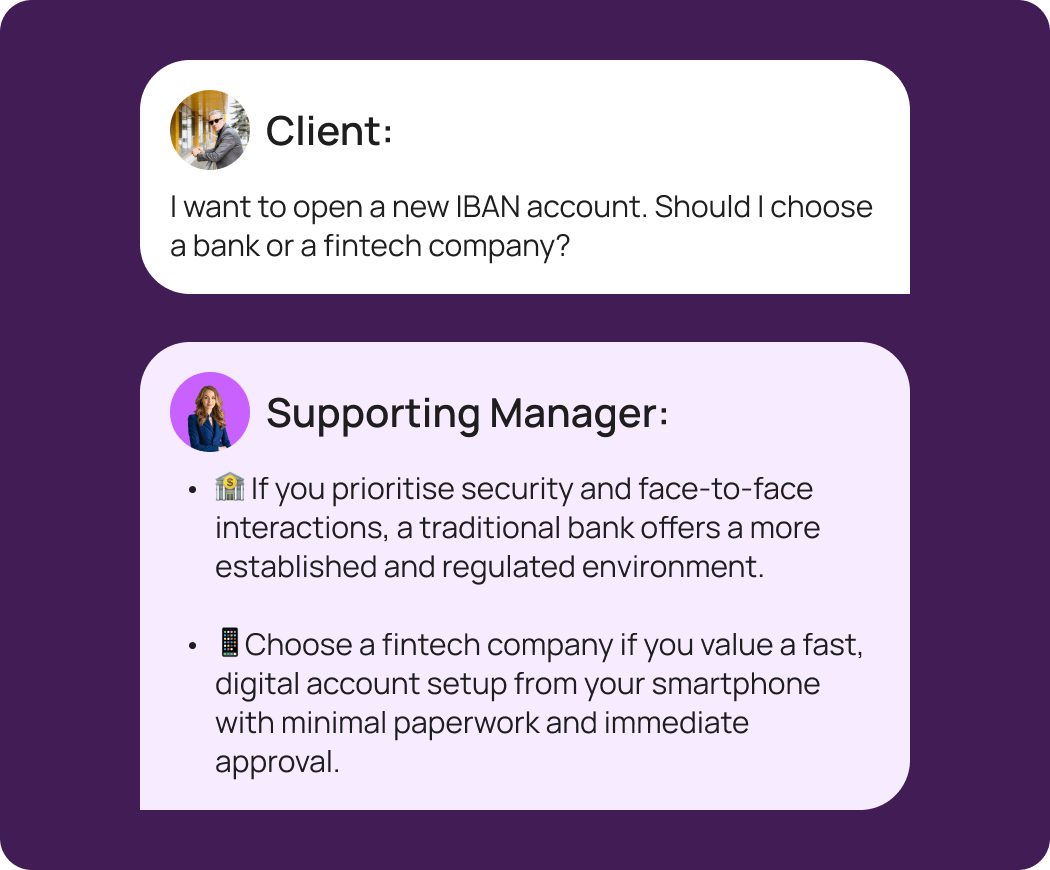
The trend in account onboarding is shifting rapidly towards digital solutions.
This trend is driven by a transition in user behaviour, with more people choosing the ease and speed of opening a virtual account provided by fintechs. According to the BAI Banking Outlook Special Report, 65% of customers are projected to engage with banks via digital channels — such as mobile apps, online platforms, and ATMs — reflecting a strong shift towards managing financial interactions without stepping into a physical office.
This influences the financial industry by accelerating the technological advancement of banking services, such as implementing blockchain for secure transactions, and pushing institutions to invest in technology and digital platforms, like AI-driven chatbots.
User Interface and Experience
The differences between banks and fintech companies become even more apparent in how you interact with their services. A user-friendly interface may make everyday tasks like checking balances, executing monetary transfers, and setting up savings goals faster and more effective.
How does the user experience in the banking and FinTech sectors differ from one another?
Banks: The legacy challenge
Traditional banks have been associated with internet platforms that often struggle with outdated interfaces. Common user complaints include:
- Cluttered and confusing layouts;
- Slow loading times;
- Limited mobile functionality;
- Difficulty finding specific features or information;
- Complex navigation menus.
Using a bank’s digital platform is akin to trying to operate the DeLorean time machine from “Back to the Future” without a manual: despite the potential for great functionality, the legacy interface and slow responses can make you feel like you’re stuck in the past.
+ Traditional banks generally offer robust security protocols and comprehensive customer support which ensure that users can resolve issues when navigating their online banking systems.
– Users often report frustration with having to click through multiple pages to complete simple operations such as balance enquiries or making a transfer. Some banks still require special hardware tokens or complex login processes, adding another layer of inconvenience.
Fintech: The user-centric approach
In contrast, fintech platforms are designed to offer intuitive navigation. They focus on delivering simple online banking experiences. These platforms cater to digitally empowered users with:
- Clear, intuitive mobile app interfaces;
- Easy-to-find features and information;
- Seamless integration between services;
- Biometric login options, like fingerprint or face recognition.
Navigating a fintech app is like stepping into the intuitive user experience of Tony Stark’s Iron Man suit: everything is intuitively designed for optimal usability, with integration of features that make managing your finances feel almost effortless.
+ Fintech platforms often allow users to complete tasks such as sending money, checking spending analytics, or setting savings goals with just a few taps.
– However, the rapid pace of technological updates in fintech apps can sometimes lead to frequent iterations in user interface design, which may cause confusion.
Transferra’s approach to user experience centres on providing a highly intuitive platform for financial management, combining real-time currency exchange, multi-currency account support, and enhanced security features.

The trend in banking customer engagement is increasingly leaning towards digital solutions.
This trend is driven by technological advancements in mobile and cloud computing. Fintechs are leading in terms of client satisfaction due to their emphasis on modern, user-friendly designs. For example, companies like Chime and Varo have achieved satisfaction rates of nearly 90% for their apps, significantly higher than the 78% national average, as reported in the Rivel Banking Research Q1 2024 survey of 280,000 U.S. consumers.
This is pushing the industry to rapidly innovate their platforms, such as integrating advanced AI for personalised financial advice, and prioritising seamless, intuitive user experiences, like offering one-click payments and easy-to-navigate banking applications.

Geographic Restrictions
Another key difference between traditional banks and fintech companies lies in their approach to geographic restrictions and residency requirements. This can affect how easily you can access, open, and manage your accounts, as well as the level of support you receive.
How will geographic restrictions stand out between FinTech and traditional banking?
Banks: Local focus
Traditional banks often have strict requirements regarding a client’s connection to the country where the account is opened. This can lead to challenges accessing financial services, including:
- Proof of address requirements;
- The need for a minimum residency period in the country;
- Restrictions on services for foreign clients.
Dealing with banks’ geographic limitations is like Tom Cruise navigating a room full of lasers in “Mission: Impossible”. They can feel like an obstacle course if you’re not firmly connected to the area.
+ Traditional banks provide strong local support and are well-versed in regional regulations, which helps them ensure compliance and manage risks effectively for domestic customers.
– These requirements can be challenging for international professionals and expatriates, who might find cross-border banking services limited.
Fintech: Global outlook
Many fintech firms allow users to open accounts regardless of their physical location, making them an attractive option for expatriates and frequent travellers. This approach offers:
- Easier account opening for non-residents;
- Multi-currency financial instruments;
- Enhanced cross-border payment capabilities.
Fintech companies offer a global outlook and flexibility similar to James Bond’s ability to travel anywhere in the world without being constrained by borders or bureaucracy.
+ Fintech firms provide versatile account setup processes, enabling users to manage finances effortlessly from anywhere and offering features like seamless international transfers.
– Fintech companies must follow regulations, which vary by country. Some services may be restricted based on your location or citizenship.
Transferra provides global financial solutions but excludes high-risk and sanctioned countries to ensure regulatory compliance.

The trend in cross-border banking is shifting towards greater flexibility.
This trend is driven by the increasing globalisation of the economy, fuelled by factors such as trade, investment, and migration. According to FXC Intelligence, transnational payment flows reached about $146 trillion in 2023, reflecting a rising demand for international financial operations, particularly in regions with robust digital infrastructure, such as India and Brazil.
This is driving banks and digital financial service providers to enhance their international offerings and adapt to diverse regulatory environments, like complying with varying data protection laws.

Safeguarding Customer Funds
When choosing a financial partner, it’s crucial for you to understand how your funds are protected in the event of bankruptcy or financial issues. This awareness helps prevent situations where your money could be lost or inaccessible.
How do banks and fintech companies safeguard client funds?
Banks: Deposit insurance schemes
Banks offer deposit insurance to protect clients’ funds, usually up to a specific limit. This safety net, however, may not cover all the money in an account:
- In the United States, almost all bank deposits are insured up to $250,000 per depositor per insured bank by the FDIC;
- In Germany, deposit insurance is provided through the ESFGD, guaranteeing up to €100,000 per depositor at one bank.
- In the United Kingdom, the FSCS covers up to £85,000 per depositor across all accounts at one institution.
- In Switzerland, FINMA guarantees up to CHF 100,000 per depositor at one bank.
Bank deposit protection schemes are like the limited number of lifeboats on the Titanic. Just as there weren’t enough lifeboats for all passengers, deposit insurance has a cap, and any funds exceeding this amount are not secured to be covered.
+ If the bank fails, your capital is protected up to the insured amount. The government guarantees you’ll get your money back within that limit.
– However, it is important to note that there are limits to the protection, and some investments and other products may not be covered.
Fintech (with EMI licence): Segregated accounts
Fintech companies, especially those with Electronic Money Institution (EMI) licences, handle client funds differently. They keep these funds in separate accounts. Key differences:
- Banks can lend out deposited money, while fintechs typically can’t;
- Bank protection is usually government-backed, while fintech safeguarding relies on proper account segregation.
Similar to the safety protocols in “Jurassic Park”, fintech companies create isolated environments for client funds, ensuring that even if something goes wrong in the main system, your money remains untouched and secure.
+ Clients’ money is not used for loans or operational expenses.
– Fintech protection may lack the government-backed guarantees that traditional banks offer.
Transferra prioritises the security of client funds by utilising segregated accounts, ensuring that customers’ money is kept separate from the company’s operational resources, providing an extra layer of protection and peace of mind.

The trend in safeguarding money is increasingly focussing on enhanced security measures.
This trend is driven by growing consumer concerns about data breaches, fraud, and monetary instability. According to the report titled “Gen Z’s Top Priorities When Selecting a Financial Services Provider” by MX and published by The Financial Brand, approximately 48% of respondents rank trust and security as top priorities when selecting a financial service provider.
This emphasis on data protection is leading financial institutions to adopt more stringent measures, such as increasing deposit insurance coverage and strengthening regulatory compliance.

Customer Support and Services
Customer support is a critical element that significantly influences user experience and satisfaction. The approach to client assistance can have a direct impact on duties like resolving account difficulties, settling disputes, and getting aid during emergencies.
What aspects of the customer experience at banks and fintech companies are the most crucial?
Banks: A reliance on call centres and in-person assistance
Traditional banks often rely on in-person customer support, call centres, and limited online assistance. Several factors contribute to the overall satisfaction of their clients:
- According to a report by GlobalBanks, poor communication and over-reliance on messaging bots can leave customers feeling frustrated and disconnected from real, individualised support;
- A lack of personalised and timely responses often leads to dissatisfaction, as сlients worry their unique demands are not being adequately met;
- The need to repeatedly provide the same information due to disconnected service platforms exacerbates customer frustration and hampers the efficiency of problem resolution.
Depending on live help at a bank can be like “Groundhog Day”, where each visit or call feels like a repeat of the last, with the same questions asked and the same details being given, but little progress made.
+ Traditional banks offer the option to speak with a representative, providing a sense of personal connection and trust during complex issues.
– However, reliance on call centres and limited online assistance can lead to slow response times.
Fintech: Digital customer support channels
Need customer support that fits your lifestyle? Fintech companies are known for their digital approach with multiple channels for assistance, including live chat, chatbots, and detailed FAQ sections:
- Round-the-clock assistance, perfect for those with irregular schedules or overseas commitments;
- Many channels of support, such as websites, social media, and mobile apps, to ensure that customers may receive assistance through their preferred method;
- Utilising consumer information to deliver proactive service and personalised recommendations, such as tailored financial product suggestions and timely notifications;
- Virtual assistants powered by AI for handling simple issues and common enquiries.
Fintech’s use of customer data for personalised insights is akin to the predictive technology in “Minority Report” — anticipating your needs before you even realise them, but occasionally missing the human touch in more nuanced situations.
+ This digital infrastructure allows fintech companies to offer 24/7 support, making it easier for users to resolve issues quickly and effectively.
– However, reliance on digital channels can sometimes lead to impersonal interactions, and complex issues may be harder to resolve without human intervention.
Transferra’s approach to customer support stands out by offering direct access to dedicated account managers, providing personalised, expert assistance rather than relying on automated chatbots.
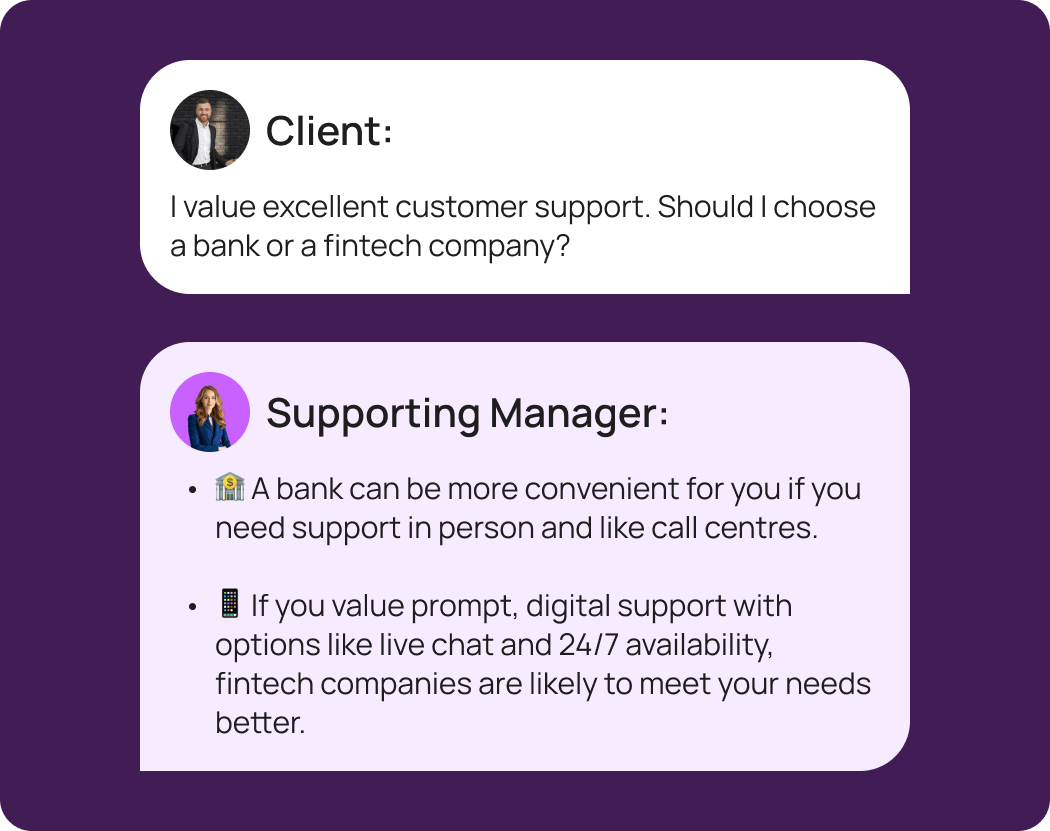
The trend in customer support is moving towards enhanced digital service options.
This trend is driven by the growing demand for instant, convenient solutions. A report by the Fintech Association of Consumers highlights that 87% of clients consider excellent customer service a vital factor when choosing a financial provider. In 2024, customer support in Europe is shifting towards online service channels. Gen Z consumers prefer phone support, while boomers are using digital chat.
This shift to digital also emphasises how important self-service solutions are becoming. In order to cut down on the necessity for direct human connection, many customers now choose to use simple internet tools to address problems on their own.

Innovations and Additional Services
When selecting a provider, consider those that excel in seamless integration across multiple platforms, including mobile apps and online services. Evaluate the variety and complexity of products available, such as savings accounts, loans, and investment options.
What technological advances distinguish fintech from banks?
Banks: Traditional product offerings
Traditional banks have long been the cornerstone of the financial industry. Their core services typically include savings and checking accounts, personal and business loans, mortgages, and wealth management solutions:
- Basic financial tools for managing daily transactions and saving money;
- Credit facilities for individual and business needs;
- Long-term loans for purchasing real estate
- Services designed to help individuals manage and grow their capital.
Just as the Millennium Falcon in “Star Wars” is a reliable but outdated vessel in a galaxy of advancements, traditional banks offer stable but slow-to-evolve financial products, lagging behind newer technologies.
+ For customers seeking peace of mind, banks provide an extensive range of dependable, tried-and-true services that address both simple and complicated financial demands.
– Despite these innovations, traditional banks often lag in agility and speed when compared to fintech companies, largely due to their size and regulatory constraints, resulting in less responsive product offerings.
Fintech: Innovative features and integrations
Fintech companies are known for their agility and innovative approach to financial services. They have introduced a range of new features that are not only user-friendly, but also cater to specific customer needs:
- Peer-to-peer payment systems;
- Robo-advisors for investment;
- Blockchain-based transactions;
- Open banking APIs that allow for smooth connectivity with other services.
Just as Joseph Cooper in “Interstellar” navigates through a wormhole to discover new worlds, fintech companies use cutting-edge technology to transport users to advanced financial solutions.
+ By focussing on customer-centric solutions and leveraging data analytics, fintech companies provide a more tailored experience compared to traditional banks.
– However, the rapid pace of innovation and reliance on emerging technologies can sometimes lead to stability issues and regulatory uncertainties.
Transferra transforms financial management by offering a multi-currency IBAN account that integrates with global payment networks like SWIFT and SEPA, coupled with real-time transaction capabilities across 180+ countries.

The trend in financial technology is characterised by heightened competition driving rapid innovation and expansion of services.
This trend is driven by the need for financial institutions to stay competitive and meet evolving customer expectations, as highlighted by research from Aite-Novarica Group, supported by Finastra, which indicates that around 94% of banks plan to invest more in modern systems to support increasing demand for enhanced payment capabilities. Fintechs are actively adopting new technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence.
This increasing competition results in lower fees and improved service quality for consumers.

Fees and Pricing Structures
Look for providers that offer clear, transparent pricing with minimal hidden charges, as this can greatly impact the overall cost of banking solutions. Consider how fees are structured, including account maintenance fees, transaction fees, and costs for additional services.
What are the bank and fintech transaction fees?
Banks: Traditional fee models
Traditional banks typically have a variety of fees associated with their services:
- Monthly maintenance fees for maintaining a checking account. These fees typically vary from $5 to $15, depending on the bank and the type of account;
- Overdraft fees when an account balance goes below zero. These fees typically cost between $30 and $35 per occurrence, which can add up quickly if not managed carefully;
- ATM fees outside of a bank’s network often result in additional charges. These fees can vary but are commonly around $2 to $3 per transaction;
- Wire transfer fees may range from $10 to $30, depending on whether the transfer is domestic or international.
Much like Katniss Everdeen in “The Hunger Games” faces constantly shifting rules and hidden traps, banking customers encounter a fee system that is difficult to understand, with the potential for hidden charges and unexpected costs hidden beneath the surface around every corner.
+ Traditional banks may provide personalised fee structures based on the account holder’s relationship, such as loyalty discounts or preferential rates for long-term clients, which can be beneficial for regular patrons.
– However, the lack of transparency and potential for high fees can lead to unexpected expenses and complicate budgeting for customers.
Fintech: Often lower fees, transparent pricing
Many fintech services, such as digital wallets, peer-to-peer payment systems, and online-only banks, provide low-cost or no-fee options for basic transactions:
- Some digital banks do not even charge monthly maintenance fees or ATM fees;
- Clarity and simplicity in pricing make it easier for customers to understand what they are paying for;
- Transparent foreign exchange (FX) fees allow users to see upfront costs;
- The rise of real-time payments (RTP) and account-to-account (A2A) transfers is reducing reliance on intermediaries, potentially lowering transaction fees.
Fintech pricing is like the efficient resource management of the spaceship Nostromo in “Alien”: it’s designed to minimise waste and cut costs. Still, just as the crew faces unexpected challenges aboard the Nostromo, users of digital financial services might encounter fees for premium services.
+ This clarity and reduced cost structure are key advantages that attract consumers to fintech services.
– While fintech platforms often provide basic services at no charge or at a low cost, they may impose fees for advanced features such as increased transaction limits or currency conversions.
Transferra offers clear, itemised pricing with a fixed monthly fee and transparent costs for transactions and additional services.

The trend in pricing within the financial services is characterised by increasing transparency and lower fees.
This trend is driven by the escalating competition between traditional banks and fintech firms, alongside increasing regulatory pressures to enhance transparency, leading to a more consumer-friendly pricing structure. Visibility of global financial operations poses a challenge to over 80% of companies, and more than 60% are dissatisfied with the clarity of their current provider charges (EY internal global research 2022).
This focus on transparency and reduced costs is particularly appealing to younger consumers who actively use digital platforms for financial management.
Regulatory Environment
When choosing a provider for opening an account, pay attention to how the company complies with regulatory requirements across different jurisdictions. Consider the provider’s licensing, adherence to local laws, and the ability to adapt to changes to new policies.
What steps should fintech and banks take to ensure regulatory compliance?
Banks: Established regulatory framework
Traditional banks operate under a well-defined and mature regulatory framework. These regulations encompass a wide array of standards:
- Basel III Regulations aims to strengthen bank capital requirements, enhance risk management, and improve financial institution liquidity;
- European Central Bank (ECB) Regulations focus on maintaining financial stability and protecting consumers;
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Counter-Terrorist Financing (CTF) Regulations require banks to implement strict measures to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
The regulatory landscape for traditional banks is akin to the rigorous safety protocols aboard the spaceship Discovery One in “2001: A Space Odyssey”: it’s designed to safeguard against unforeseen risks and ensure stability, though it may sometimes feel overly restrictive.
+ These changes ultimately contribute to a safer and more robust financial ecosystem.
– Customers may experience more rigorous identity verification processes and need to provide additional documentation when opening accounts or conducting large transactions.
Fintech: Evolving regulations, challenges, and opportunities
Fintech legislation is more flexible and constantly developing. The EU Digital Finance Package is a key regulation impacting the industry in Europe:
- The Markets in Crypto Assets Regulation (MiCA) establishes a unified set of rules for issuance, trading, custody, and disclosure of crypto assets at the EU level, including cryptocurrencies, security tokens, and stablecoins;
- The Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) Pilot Regime allows companies to develop and trial innovative blockchain-based products and services in a controlled environment;
- The Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) outlines requirements for the digital functions of financial institutions, focussing on risk management, incident response, and cooperation with regulators.
The fluid nature of fintech regulations can be compared to the ever-changing rules of the game in “Jumanji”. As players in the movie must adjust their strategies to the game’s unpredictable twists, fintech firms need to remain agile and responsive to evolving demands.
+ For clients, this means the security and transparency of their investments, ensuring a more regulated and resilient financial environment.
– However, the dynamic and developing nature of these regulations can create uncertainty and complexity, potentially leading to increased compliance costs.
Transferra is committed to maintaining compliance with all relevant laws and regulations, including Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing measures, adhering to UK, European, and international standards.
The trend in the regulatory environment globally emphasises a balance between innovation and compliance.
This trend is driven by the need to balance technological innovation with financial stability and security concerns. This need comes from the growing global economic connections and the rising threat of illegal financial activities. An alarming estimate from the United Nations indicates that illegal proceeds account for 3 to 5% of the world’s GDP, underscoring the critical importance of robust regulatory frameworks to combat these risks and protect the global economic system.
For users, this means access to more innovative and reliable financial products, such as blockchain-based payment solutions, and greater protection of their personal and sensitive data.

Bank or Fintech: Final Thoughts
When comparing banks and fintech companies, it’s important to understand the differences in how they operate and the benefits they offer. Each has its own strengths and considerations, which can impact your experience as a user:
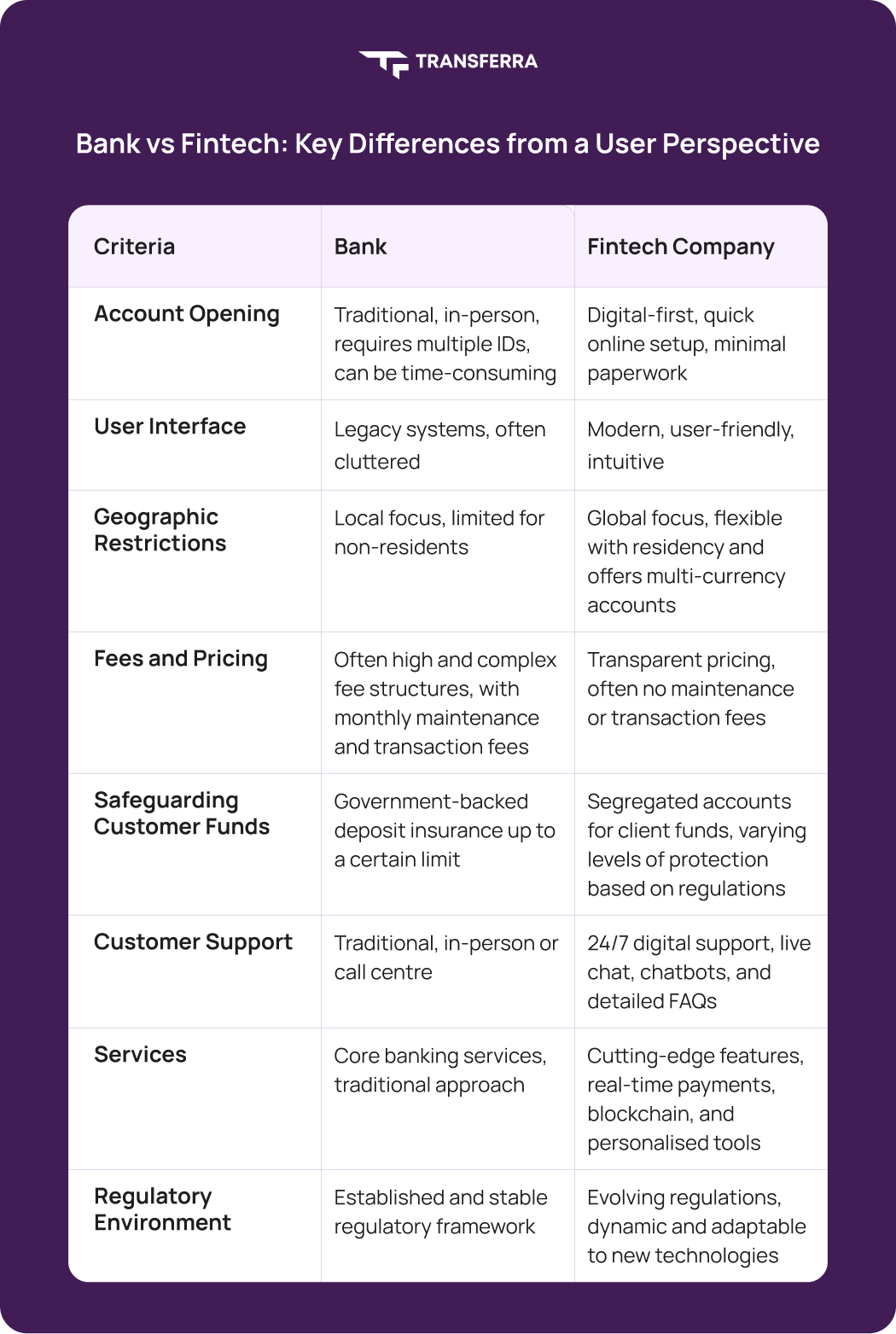
- Banks provide traditional services and often require physical visits, but they excel in local compliance, strong deposit insurance, and face-to-face support. Their fee structures can be complex, but they are backed by well-established regulations.
⠀ - Fintech Companies offer modern, digital experiences with intuitive apps and flexible services like multi-currency accounts. They typically provide lower fees or no-cost options for basic transactions. However, their regulatory environment is still evolving, which can present both opportunities and challenges.
Ultimately, the choice between banks and fintech depends on your priorities for convenience, security, and cost-efficiency.
Recommendations:
- Choose a bank if you value traditional, in-person interactions, a stable regulatory framework, and established safeguards.
⠀ - Choose a fintech company if you prefer a fast, digital account setup, innovative features, reduced costs, and more flexibility with geographic restrictions.
⠀ - Choose a Transferra if you prioritise digital convenience and need a seamless online platform with a user-friendly mobile app, particularly in the context of international banking.

