Decoding Bank KYC Requirements: Users’ In-Depth Guide
Unlock Bank KYC Requirements with this user-friendly guide from Transferra. Ensure a secure and informed banking journey in a concise read.
What financial pathways have to offer is the preservation of transactions. In this field, KYC or Know Your Customer is in the leadership. As it has been built with defince mechanisms, KYC proves to be an important safety against violation of anti-money laundering principles. This article will investigate the intricacies of KYC Protocols, which strive to collect client data for advanced security procedures.
What is KYC in Banking?
The KYC is a part of the wider Anti-Money Laundering scheme and serves as an initial fortification against financial crimes. It is a two-step procedure that involves customer information collection and data validation.
By applying a document-based approach, organizations meticulously review the validity and authenticity of identity documents as well as address-proof documents through a verification process aligned with global KYC standards. A utility bill is usually considered as proof of address.
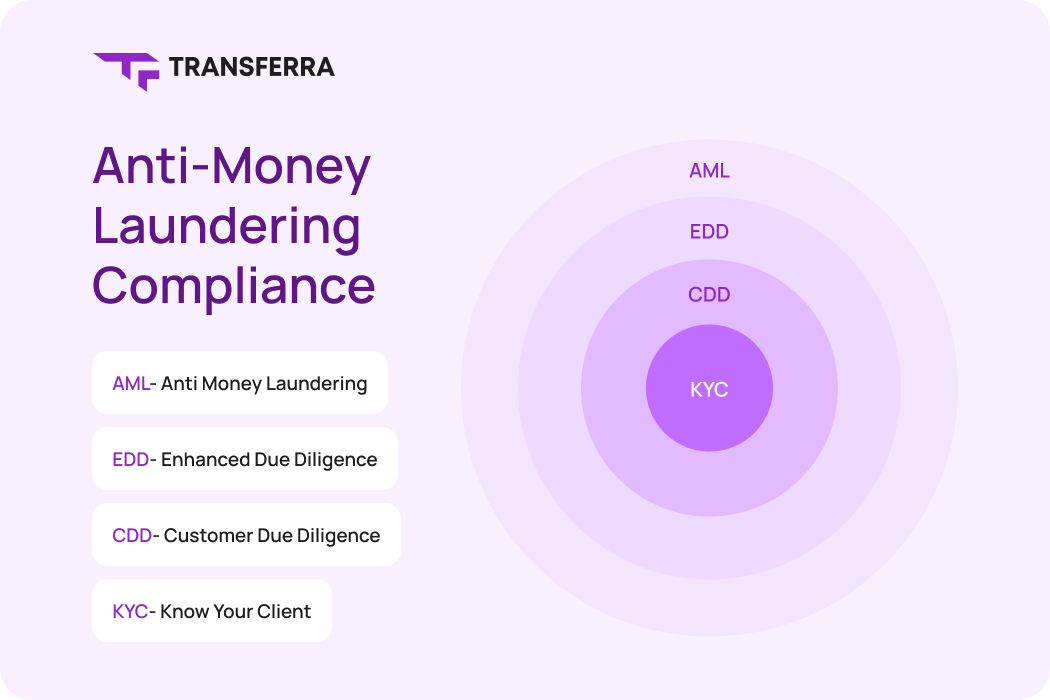
What is AML Compliance?
AML compliance refers to regulations and actions aimed at combating money laundering and financing terrorism. These regulations, which originated in the 1970s and 1980s got momentum when financial institutions were found to be money laundering machines. Organized crime along with the weaknesses of uncontrolled financial systems led to developing the first anti-money laundering laws. AML compliance works together with governments and financial institutions to minimize fraudulent activities, thus contributing to the maintenance of global integrity in the finance sector.
For banks and non-banking financial institutions alike, AML compliance is non-negotiable. Here’s why:
- Preventing Money Laundering: AML compliance shields against money laundering by identifying and deterring illicit financial activities.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Countering Terrorist Financing: Key to AML, it thwarts the financing of terrorism through monitoring and reporting suspicious transactions through robust transaction monitoring mechanisms.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Maintaining Regulatory Compliance: Mandated by regulators, AML compliance ensures adherence to legal standards, with non-compliance resulting in penalties.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Enhancing Global Security: AML regulations promote global cooperation, standardising practices to combat financial crimes on an international scale.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Protecting Institutions and Customers: Beyond regulatory obligations, AML compliance instills confidence in customers, assuring them of secure and transparent financial dealings.
Implementing KYC: Who Bears the Responsibility?
The responsibility for implementing KYC spans multiple sectors, emphasising a collaborative effort to protect the financial landscape from fraudulent activity. Everyone, from traditional banks to emerging cryptocurrency platforms, is responsible for ensuring the KYC process’s integrity:
- Financial institutions including banks and credit unions are mainly charged with the responsibility of ensuring that strong KYC mechanisms have been put in place regarding customer verification and identification.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Non-banking financial institutions such as insurance companies, investment firms and money service businesses are also supposed to secure their transactions by ensuring compliance.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Cryptocurrency exchanges should have the KYC processes implemented to increase security and answer the regulators’ requirements, although most of them may seem decentralised.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Corporate organizations that engage in financial transactions. Whether mergers, acquisitions or partnerships KYC processes enable the establishment of credibility for businesses as well as their owners.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Governing organizations put in place the directives and rules that financial institutions must adhere to for security assurance of customer identification. Thus, they too need to adopt KYC procedures.
KYC does not only apply to entities that are subject to AML legislation. Those businesses that may benefit from KYC include e-commerce platforms, renting services and freelance websites among others. It is useful in two different ways as a way of deterring suspicion would be-behaving individuals and validating risky suppliers or worse, online platforms with no direct AML regulations.
KYC and KYB: What is the difference?
Though both are examples of Due Diligence systems, KYC and KYB serve separate roles in the identity verification process for individuals versus entities. Here’s a concise breakdown of the main differences:
| Key Differences | KYC | KYB |
| Scope | Primarily focused on individual customers. | Focusing on businesses and corporations. |
| Information Gathered | Involves personal details of individuals. | Business-specific information such as ownership data, form of legal structure and financial position. |
| Verification Process | Document checks and individual identity verification. | Documentation regarding legal status, ownership and financial document holds the set of business identity verification. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Facilitates compliance with laws concerning single customers. | Provide compliance with rules on business enterprises. |
For banking, the KYC process requires obtaining specific personal information that confirms not only affiliate identity but also every factor of a customer’s identification. Here are the key KYC requirements:
- Personal Information: In this case, customers need to disclose some information about themselves such as name and surname, date of birth, and address.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Government-issued Identification: This can be a driver’s license, passport or national ID. The establishment checks the identity particulars against those on these documents.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Proof of Address: To prove the given address, customers are usually required to present proof of residence. Common documents are utility bills, rental agreements or bank statements with the name and address of the customer.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Photograph: Usually KYC includes a current passport-sized photograph. This helps with visual identification and adds another level of security verification.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Tax Identification Number (TIN): Customers may be required to give the Tax Identification Number (TIN) based on jurisdiction to comply with tax regulations. This makes the financial activities of customers traceable and transparent.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Occupation and Source of Income: Banks could ask customers about their careers and how they generate income. This information assists in an assessment of the customer’s financial record and allows compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) procedures.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Purpose of the Account: Defining the purpose of an account is a typical KYC requirement. This information allows banks to find further analysis and risk assessment, which will enable effective management of the banking relationship about savings, business or investments.
KYB Requirements for Business Customers
For businesses that operate under financial institutions, it is important to ensure they have clarity and legality of corporate entities. Here’s a dedicated exploration into KYB requirements tailored for business customers:
- Business registration documents: Companies usually need to show documents that prove their legality. This includes certificates of employment, business licenses and relevant permits.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Ownership Structure: Information about the ownership hierarchy of a business is needed. Notably, it involves revealing details on major shareholders, beneficial owners and people who have significant control over the business.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Articles of Association: The Articles of Association issued refer to the internal regulation accepted by the company concerning it. Therefore, this document helps to understand the legal environment in which the business is run.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Business Address: Confirmation of the business address for this company guarantees that it corresponds to what has been reported. Most of the time, utility bills or government documents proving where a business is located are needed.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Tax Identification Number (TIN): Like individual orders, businesses are sometimes required to specify their TIN to meet tax regulations. This facilitates economic activities.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Purpose of business accounting: Regardless of aggregate employment, payroll or individual transactions, this information assists in shaping the bank’s activities according to business needs.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Operating financial statements: Financial institutions could request recent financial statements that will be provided to validate the current state of the business’s finances. These include the balance sheet, the income statement and the cash flow.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Enhanced due diligence (EDD) for high-risk companies: In the case of high-risk businesses, a company operating in critical industries that are susceptible to money laundering or fraud can undergo advanced due diligence conducted by analyzing project activities and associated risks.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Anti-bribery and corruption (ABC) compliance: Companies may have to show evidence of observing anti-bribery and corruption legislation. It has adopted measures in policies and procedures to curb vices within the organisation.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Ongoing audits: The high-risk positions can be constantly audited by financial institutions. This facilitates timely and considered modifications of project design or operations.
Traditional Banking vs. Fintech Onboarding with Digital KYC
Digital KYC separates fintech from traditional banks by redefining onboarding. Fintech functions well in delivering smooth and timely digital services with advanced technology, online connectivity, and user-friendly process effectiveness. Conversely, branch-centric traditional banks can often pose significant challenges in opening accounts – especially to foreign customers due to their offline professional process while the Fintech onboarding experience online system demonstrates the difference between the two experiences and suggests the paradigm shift of accessibility and operational efficiency.
The main features of the digital KYC process are:
- Remote Authentication: Customers do not have to be physically present because they can authenticate themselves remotely. Video calls, biometric scanning and sophisticated verification technology make the process safe yet seamless.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Document Authentication: With the help of advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence, identity documents can be processed at a higher speed with increased accuracy. Machine learning systems help identify and validate documents, mitigating fraud risks.
⠀⠀⠀⠀ - Biometric Identification: Biometrics including fingerprint, facial recognition and voice authentication provide another layer of protection. These biometric identifiers make the customer authentication process more precise and cautious.
Transferra’s Swift and Secure Onboarding
In Transferra, we reinvent the onboarding journey via a completely digital process that smoothly combines such aspects as speed, security and consent. Further, with our user-oriented approach to service provision, the journey takes only fifteen minutes and you have all financial services at your disposal. Explore the key features below.
Expedited processing: With our endemic digital onboarding system, people need not fill out cumbersome papers and wait to process information before accessing financial services.
Corporate Excellence: With that, our corporate client application brings with it additional functionality for easy information dissemination about the entire company. We simplify the addition and retrieval of data for owners that constitute representatives as well as ultimate beneficiaries (UBO) owning above 25% of a firm.
Biometric Verification: Our user-friendly biometric authentication, which includes registration by easily taking a selfie, provides more security. The users can have peace of mind knowing that the delicate information is treated with a lot of care and due diligence.
To know everything about our KYC and KYB processes, research out a well-structured onboarding guide. Register an account with Transferra today to start a smooth financing process developed specifically for your business needs. Take your financial experience to a higher level with enhanced speed, security and convenience.