TARGET2 cross border payments: a full guide
TARGET2 is a payment system that is used for large-value transactions in the European Union. Here’s everything you need to know about TARGET2.
TARGET2 is a payment system that is used for large-value transactions in the European Union. It was introduced in 2008 as a replacement for the first-generation TARGET (Trans-European Automated Real-time Gross Settlement Express Transfer) system. The main purpose of TARGET2 is to facilitate the settlement of cross-border payments between banks in the European Economic Area (EEA), ensuring that funds are transferred quickly and securely. In this article, we will take a closer look at TARGET2, including how it works, its key features, and its impact on the European financial system.
How was TARGET2 adapted?
TARGET2 was introduced as a replacement for the original TARGET system, which was launched in 1999. The original system was designed to facilitate cross-border payments within the Eurozone, but it quickly became clear that the system was not scalable enough to handle the growing volume of transactions. As a result, the European Central Bank (ECB) decided to develop a new system that could better meet the needs of the financial industry. The result was TARGET2, which launched in 2007 and has been in use ever since.
How does TARGET2 work?
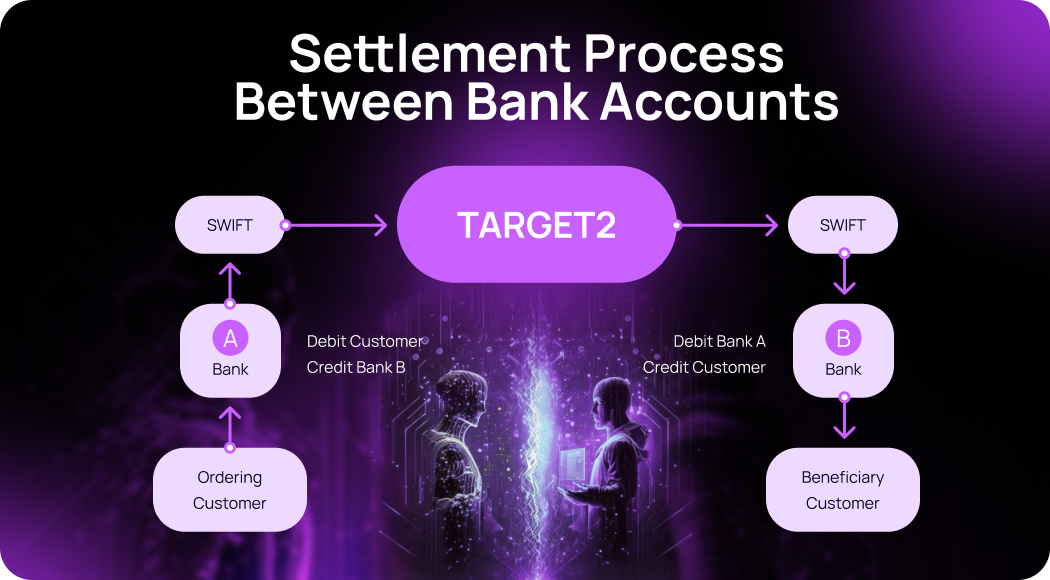
TARGET2 operates on a real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system, which means that transactions are settled on a one-to-one basis in real-time, rather than in batches. This ensures that transactions are processed quickly and efficiently, with minimal risk of errors or delays.
To use TARGET2, banks need to have an account with a national central bank that is part of the system. When a bank initiates a transaction, it sends a payment order to the central bank, which then sends the order to the recipient bank. Once the recipient bank confirms receipt of the payment, the funds are settled in real-time.
TARGET2 supports multiple currencies, including the euro, Swedish krona, and Swiss franc. This makes it a popular choice for cross-border transactions within the European Economic Area, as it allows banks to settle transactions in the currency of their choice.
In addition to facilitating cross-border payments, TARGET2 also supports domestic payments within each participating country. This means that banks can use the system to settle large-value transactions within their own borders, as well as across borders.
TARGET2 is considered to be one of the safest and most reliable payment systems in the world, with robust security measures in place to protect against fraud and other forms of cybercrime. As a result, it is trusted by banks and financial institutions throughout the European Union and beyond.
TARGET2 platform also works every day except on Saturday and Sunday from 07:00 to 18:00 CET except on some public holidays like New year’s day, Good Friday, Easter Sunday, etc.

Real-time gross settlement
Real-time Gross Settlement (RTGS) is a payment system that facilitates the instantaneous settlement of high-value transactions between banks and financial institutions. RTGS operates on a real-time basis, meaning that transactions are settled as soon as they are processed, rather than being batched and settled at a later time. This allows for faster and more efficient transactions, as well as greater security and reduced settlement risk.
RTGS systems typically handle large-value transactions, such as interbank transfers, securities settlements, and foreign exchange transactions. In addition to facilitating transactions, RTGS systems also provide a range of related services, including messaging, reporting, and settlement confirmation. Overall, RTGS is an important tool for enabling secure and efficient financial transactions at the institutional level. As of 2022, the system is used by over 52,000 banks including branches and subsidiaries.
Objectives of TARGET2
TARGET2 was established by the European system for participants’ intermediaries to use it for gross settlement in central bank money when a large amount of money is involved in transactions such as interbank payments, monetary policy operations, and ancillary system transactions.
The Eurosystem later gave the “3CB” (Banca d’Italia, Deutsche Bundesbank, and Banque de France) the role of developing the SSP which will serve as a gateway through which participants will register their accounts with central banks. Note that this is simply to make transactional easy and seamless across European countries.
Generally, the objectives of TARGET2 include:
- The implementation of the Euro’s system of monetary policy and the functioning of the Euro marketplace.
- Reducing systemic risk to the minimum without deviating from the payment plan i.e the possibility of a single factor causing an entire market to collapse.
- Ensuring smooth transfer of payments in euros.
By implementing these objectives TARGET2 ensures safe and transparent payment options across Europe contributing to the stability of the Euro in the financial market.
Who are the TARGET2 participants?
TARGET2 replaced TARGET and became the next giant in processing transactions within the euro area. However, the number of participant states within the Euro area keeps increasing when new features are added to the platform. Some EU member states which have not adopted the system have now decided to go for it.
However, TARGET2 has specific guidelines including access requirements that allow participants to choose configuration based on their purpose. The participants of TARGET2 are majorly European countries. The participants can choose to access TARGET2 via the following means.
Direct participant. The direct participant is a financial institution in the European Economic Area (EEA) that holds the Euro central accounts and can send and receive payment themselves or on behalf of their clients.
Indirect participant. This one only sends and receives payment using the direct participant to TARGET2 has access.
Multi-addresses access. This includes subsidiaries and branches of direct participants in TARGET2. They are permitted to channel payment through the account of the direct participants.
It should be noted that more than 1000 financial institutions in EEA are direct participants while over 52,000 banks are subsidiaries and branches that make use of the direct participant accounts. Also, some financial institutions in non-euro countries join TARGET2 to make euro payments to their clients when the need arises.

Differences between Euro1 and TARGET2
Euro1 and TARGET2 are both payment systems used in the European Union, but they have some key differences.
Euro1 is a large-value payment system that allows for the processing of cross-border and domestic euro-denominated transactions. It is designed for interbank transactions with values above €2,000,000, and settles transactions on a same-day basis.
TARGET2, on the other hand, is a real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system that facilitates the settlement of large-value euro-denominated transactions between banks and financial institutions. It allows for the settlement of both cross-border and domestic transactions, and operates on a real-time basis, meaning that transactions are settled as soon as they are processed.
One of the main differences between the two systems is their focus. Euro1 primarily serves the needs of banks and financial institutions for large-value, same-day payment processing, while TARGET2 is more focused on providing real-time gross settlement for large-value payments. Another key difference is that Euro1 settles transactions on a same-day basis, while TARGET2 settles transactions on a real-time basis.
What are the differences between SEPA and TARGET2?
SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area) and TARGET2 (Trans-European Automated Real-time Gross Settlement Express Transfer System 2) are both payment systems used in Europe, but they differ in several ways.
Purpose: SEPA is designed to simplify and standardize euro-denominated electronic payments within the European Union, whereas TARGET2 is designed for high-value interbank payments between financial institutions across Europe.
Payment types: SEPA supports retail payments, such as direct debit and credit transfers, while TARGET2 supports large-value, time-critical, and high-priority payments.
Settlement mechanism: SEPA uses a net settlement mechanism where payments are batched together and settled in one go, while TARGET2 uses a real-time gross settlement mechanism where each payment is settled individually and immediately.
Processing time: SEPA payments can take up to one business day to process, while TARGET2 payments are settled in real-time.
Coverage: SEPA covers all 27 EU member states plus Norway, Iceland, Liechtenstein, Switzerland, Monaco, and San Marino, while TARGET2 covers all EU member states plus Iceland, Norway, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein.
How does TARGET2 differ from SWIFT?
TARGET2 and SWIFT are both payment systems, but they have some key differences.
TARGET2 is a real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system owned and operated by the Eurosystem, which consists of the European Central Bank and the national central banks of the Eurozone. It is primarily used for large-value transactions, such as interbank transfers or large corporate payments, denominated in euro.
SWIFT, on the other hand, is a messaging network used by banks and financial institutions around the world to exchange financial messages, including payment instructions. It is not a settlement system, but rather a means of communication between banks. SWIFT messages can be used to initiate payments that are settled through a variety of mechanisms, including TARGET2.
Does Transferra suppor TARGET2?
Yes, Transferra supports TARGET2 payments.
Once you fill in the payment form for EUR payments, the system will check the IBAN. IBAN, or International Bank Account Number, includes important information, such as country code, check number, the bank’s bank code, sort code for the bank branch, and the bank account number.
What Transferra checks:
- 1. IBAN is correct.
- 2. Financial institution’s credentials.
- 3. Financial institution’s BIC/SWIFT code to see what payment methods are available to the institution in question.
Based on this, our system offers the best payment option: SEPA, SEPA Instant, or TARGET2.

