Current Payment Trends (2022)
2022 transforms payments: From analog decline to Payment 4.X, biometric authentication, and digital transactions. Explore the evolving landscape!
Are the current payment systems the same as during the pre-covid era? Simply, I would answer, No! Why? Covid-19 has expedited the digitization of the payments sector. In fact, I believe 2022 is and will serve as a turning point in how consumers and corporations make transactions. Since 2020, digitization has increased throughout business-to-business (B2B), business-to-consumer (B2C), and peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions, but the pandemic’s second full year proves that it will remain, even if patterns of spending stabilize. Stakeholders earning through payment are now striving to keep up with how consumers and businesses transact.
The Emergence of New Payment Trends
Analog payments plummeted at the start of the epidemic and will likely do so this year as prepaid, debit, and credit cards compete for market dominance. Apparently, physical cards might become extinct very soon, in my opinion. Thus, businesses must guarantee that customers can utilize their preferred payment method because of the growing digitalization. As a result, point-of-sale (POS) developers are under pressure to build multichannel systems that address both front-end and back-end requirements. Payments providers are also rushing to examine new transaction channels, achieve new segments of customers and organizations, and incorporate new equipment and transaction technologies in every part of the sector. This adaptation struggle has seen various trends in payment schemes such as Payment 4. X, biometric authentication, and digital payments. Now, let us look at each trend in detail.
Payments 4.X
This is a new payment technology, primarily used by PayPal to enhance digital connection and experience, drive data excellence, develop technology prowess and foster collaborative synergies to minimize technical debt, as the diagram below illustrates.
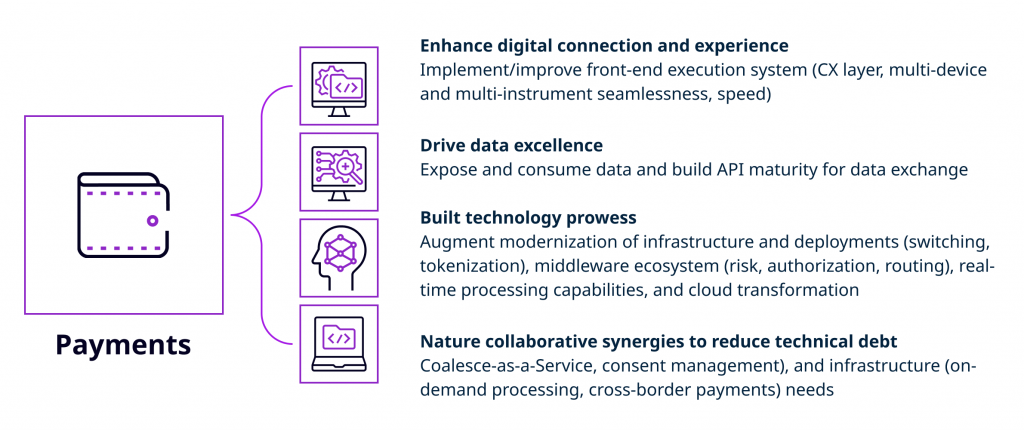
As we have experienced in previous financial crises and pandemics, businesses are expected to adjust their operations to continue operating smoothly. Similarly, Covid-19 forced the payments sector to endure a makeover, spurred by new-age firms’ innovative techniques, competitive pressures, and customers’ need for an edge-to-edge experience. As the industry crosses the barrier, it enters a new age known as Payments 4.X, where payments are integrated and undetectable and serve as an enabler for a seamless consumer experience. Digital IDs are crucial for a flawless payment experience when clients permanently change next-generation payment systems. The B2B payments field, in particular, is rapidly becoming digital. PayTechs, BigTechs, and newcomers to the market are eager to pitch in with novel solutions to assist overlooked small and medium-sized enterprises (Capgemini, 2021).
According to Capgemini, new-age enterprises strive to assume the lead in the Payments 4.X era. How do you think they do it? They are simply leveraging the popularity of non-card products and services while incumbents struggle with revenues. Firms may only realize their full market capacity by adopting open ecosystems and API-based business models because this new era requires cooperation. With the current trends, I believe that data prowess and improved payment processing skills will be required to succeed in the future. Banks and traditional payment companies are racing against the clock since their competitive edge is not guaranteed indefinitely. Besides, mergers loom as industry stakeholders seek economies of scale, while non-banks pursue new frontiers to challenge incumbents’ market dominance. While these dynamics are at work, central bank digital currency (CBDC) is growing internationally and can start a new chapter in the present payments landscape (Capgemini, 2021).
Biometric authentication
Biologists argue that everyone has a unique genetic composition. I view that that was the basis of biometrics technology. Biometric authentication is a means of verifying a person’s biological and anatomical traits. Fingerprint scanners, retina recognition, facial recognition, vein mapping, and voice recognition are examples of these verification technologies. The system typically employs two-factor authentication, where a finger scan replaces a visa or MasterCard swipe, and the user writes in a personal identification number (PIN) as normal (Katie, 2022).
Source: Katie
With the surge in crime and data theft, biometric identification might become a safe and trustworthy alternative for all electronic payments his year. In fact, this is true since you cannot access another person’s accounts without their biometrics. Biometric identification is a distinct and essential payment technique because it combines precision, convenience, and safety into one compact package. Biometric technology is a very secure approach because it utilizes unique traits. This component also contributes to developing client loyalty and trust (Gundaniya, 2022). Google Pay is one payment scheme that has significantly embraced biometric authentication technology, first introduced with Android 10. It can now authenticate transactions in the app using either face or fingerprint recognition as of version 2.100.
Deferred payments or Buy-Now-Pay-Later
Have you been in a situation where you need something, but you lack enough cash? What did you do? Deferred payments or Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL) is a system that has come to solve this issue. The system enables a customer to postpone payment on an item until later. For example, you have a month to pay off that new item if your repayment schedule expires in a month. This can be useful if your car breaks down unexpectedly or if your children destroy your windscreen, and you need a replacement item soonest with insufficient funds. Since 2019, people have been more interested in digitally deferred payments. Customers shifted to BNPL payment options in 2020 when funds were particularly tight due to Covid-19 emergence. As individuals struggled to cope with the outbreak, BNPL became a significant trend ingrained in the purchase process (Banking Circle, 2022). Flipkart, Amazon, Connect Pay, Money Tap, and PhonePe are some payment schemes that utilize this payment option.
The Rise of BNPL in Business Transactions
BNPL enables businesses to serve clients who choose to pay over time. There has been a significant shift in the payment schemes and a fundamental need to reduce payment complexity. Customers desire a seamless payment method, and companies want to satisfy their clients while lowering transaction costs and complexities. Besides, as merchants endeavor to accommodate client demand for BNPL payment options, their usage of such services has expanded. Even before the pandemic, BNPL services were gaining traction, but the growing usage of e-commerce during the pandemic has accelerated client adoption of installment payments. As a result, this payment channel attracts clients. Venture capital funding for BNPL services has soared in the last two years, and it is expected to increase even more this year. Developed payment schemes like MasterCard, Visa, and PayPal have also launched BNPL services to fulfill the changing consumer demands.
Digital payments/ Contactless payments
According to scientists, the COVID-19 virus can exist on banknotes for 28 days. Having known this, consumers have responded by adopting digital payment methods such as tap-to-pay, digital wallets, and e-commerce payments to prevent physical interaction when completing a purchase. This contactless payment technique will most likely experience fast growth in 2022. As the name implies, customers may make contactless payments by waving their smartphones across the reader. Literally, waving is faster and more convenient than inserting a card into a machine. Contactless payments are also quicker and safer than PIN payments since the encrypted data is sent instantly and directly to the point-of-sale device.
The Rise of Contactless Payments
Many firms such as Apple, Samsung, and Google, have contactless payment systems in place, including Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, and Google Pay. All you need to do to make a payment is download the app, enroll your card by inputting card information, and run your phone over any reader. Furthermore, near-field communication (NFC) technology allows for contactless payments. That is why they are often referred to as NFC payments. Many countries accept NFC payments. In China, for example, it is accepted as a means of payment for public transportation. Likewise, NFC payments are accepted in London’s bus stations. This technology is also utilized in Japan to deliver information about identification cards. This trend is expected to accelerate by 53% in 2022 (Global Payments)
Machine Learning and AI-powered security
I believe everyone desires privacy and security for his or her data. When it comes to payments, the most important factor is security. People will always choose a payment option with a high level of security. As a result, payment technologies will not progress unless they establish high-level security. Every day, payment schemes get a large amount of consumer information and payment data. Most payment schemes currently use machine learning to detect all possible risks within seconds.
To acquire artificial intelligence, you must first finish the machine learning stage. Payment schemes constantly update their software with new and varied transactions. The program learns to identify fraudulent transactions using a small collection of transactions in real-time. As the program gets more transactions, it improves its ability to recognize fraudulent activities. One of the best examples is when your bank or payment app sends you an SMS inquiring if you are aware of a transaction or not. This warning notice helps you and the payment scheme avoid critical errors that might cause monetary losses. A person does not send these texts but is sent by machine learning algorithms. The following diagram shows how payment schemes worldwide use machine learning and artificial intelligence to automate and secure their payment systems.
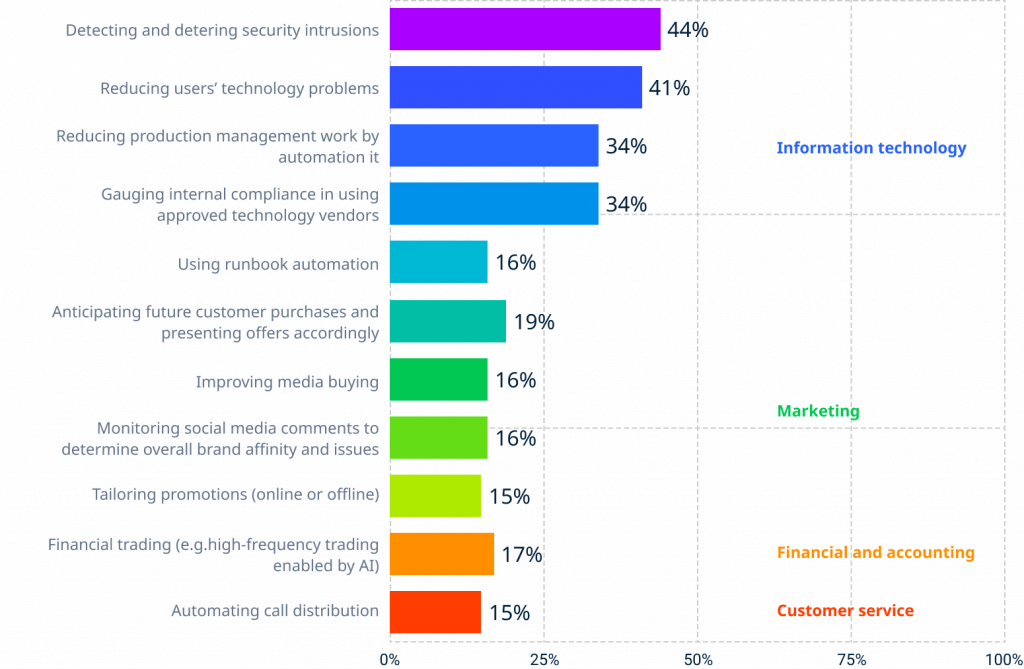
Source: Liyanage
Smart speaker payments
Sometimes, typing might be tiresome and boring. Users of smart speakers or home assistants may issue voice instructions to a device and receive a speech answer in return. The user may use voice commands to acquire real-time updates on traffic updates and weather, order from a store, and book an Uber ride, among other things.
The Rise of Smart Speakers in Payments
Smart speakers are now being manufactured and used by a slew of industry behemoths to improve your experiences. In 2014, Amazon released its first smart speaker. In 2016 and 2017, Google Home and Apple joined Amazon. However, because the speakers were limited to only phone devices, the ones that emerged from smart assistants were naturally primitive. As home automation has become popular, smart speakers have gained significant traction, especially in the payment industry.
Now let us look at some statistics to understand the smart speaker scenario better. Statista reports that 35% of consumers use smart speakers to purchase home care, food, and apparel, among other things. Surprisingly, over 28% of consumers last year utilized smart speakers to transfer money or make direct payments (Laricchia, 2022). This is not a large percentage since, for security concerns, fewer individuals use smart speakers to make payments.
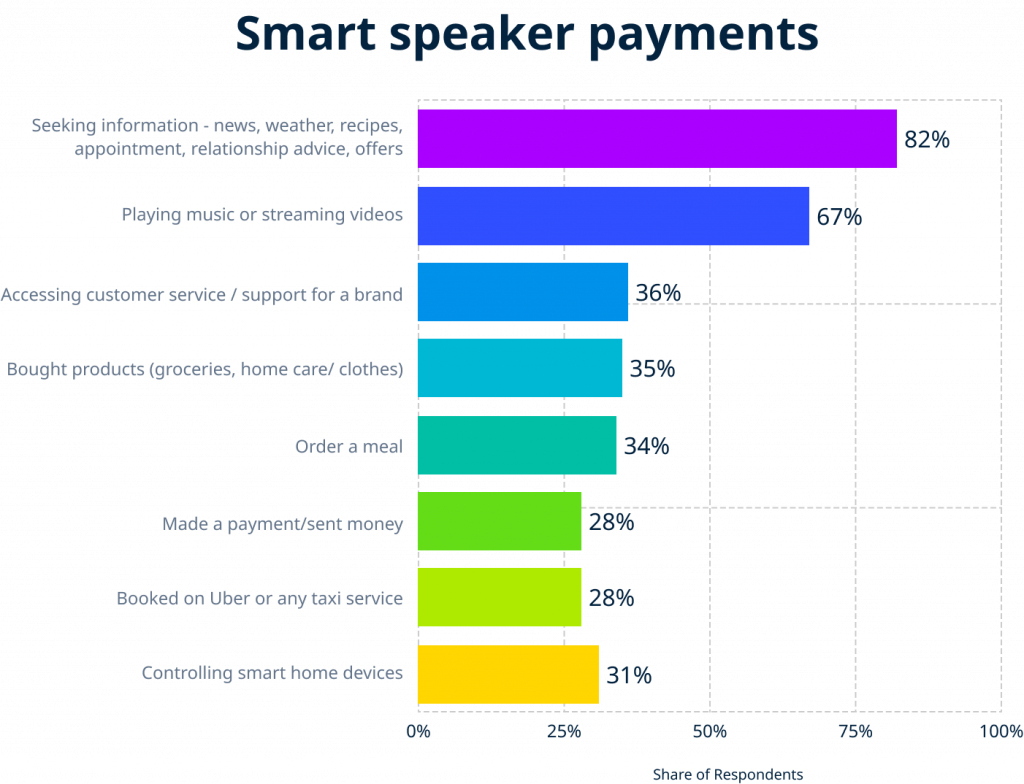
Source: Statista, 2022
According to Liyanage, 74% of consumers are concerned about security when using voice assistants to make payments. They also may discontinue paying payments because of their concerns. Despite these hitches, the future of smart speakers is bright, as major companies such as Google, Amazon, and Apple spend heavily on developing improved smart speakers. Furthermore, the statistics show that smart speaker payments have a promising future. According to Liyanage, smart speaker use will skyrocket from 18.4 million users in 2017 to a staggering 77.9 million users in 2022.
The dominance of mobile wallets
Carrying a wallet is tiresome and sometimes risky since it can get lost or get you robbed. A mobile wallet solution is just a mobile application that attempts to imitate the functionality of a physical wallet. You can send, receive, and save money in your mobile wallet, just as you do with a physical wallet. Besides, a mobile wallet may be used to pay utility bills, purchase tickets, receive incentives, and much more. In 2021, roughly 2.5 billion customers were using mobile wallets. This figure is expected to rise in 2022 and 2023 to 4.4 billion (Global Payments).
The Rise of Brand-Specific Mobile Wallets
The number of mobile wallet transactions will increase to approximately 274.4 billion this year, with more men (48%) using it than women (41%) (Finances Online). As a result, several major corporations, like Apple, Samsung, and Google, have begun to provide mobile wallets to facilitate this anticipation. However, those wallets are distinctive to a certain brand or corporation. Thus, many payment companies are attempting to develop their brand-specific wallet.
Payment firms can quickly analyze their customers’ expenditures with a mobile wallet. In a mobile wallet, there are multiple parties involved. A mobile wallet, for example, is built by a single corporation, such as Google. After that, a different company creates credit and loyalty cards. A large number of merchants also use the Google wallet. Therefore, in basic terms, a mobile wallet comprises several elements that operate together to provide simple, rapid, and cashless payment services.
Summing up Payment Trends
As the covid-19 pandemic emerged, many payment schemes changed their way of doing things. The traditional card and wallet systems are now rarely used since many payment systems are now digitalized. The development of various technologies, including Payment 4.X, biometrics, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and smart speaker systems, has facilitated this shift. Besides, the security of payment systems has been enhanced through biometric identification since no one shares biological traits with another in terms of, say, face, voice, and fingerprints. Deferred payments have also enabled customers to acquire items even without sufficient funds, considering that many people lost jobs due to the pandemic. Besides, digital or contactless payments and mobile wallets have also helped avoid the spread of the virus, thus keeping consumers safe while progressing with business.

